Unlocking Deeper Healing: Insights from Dr. Stuart Close & ACT Assessment – Presented by: Dr. Urvi Dhokiya
Executive Summary: Key Study Highlights
Patients Showed Improvement
Demonstrating positive response to intervention.
Majority Male Participants
Cohort composition with diverse age range.
Younger Adults (15-25)
Primary age group of the study population.
Understanding Bronchial Asthma: A Global and Indian Perspective
Bronchial asthma, a major noncommunicable disease (NCD) recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO), presents a significant global health challenge. Characterized by recurrent episodes of breathlessness and wheezing, its impact varies greatly among individuals, often compounded by chest tightness and a persistent cough that can worsen with physical exertion or during nocturnal hours, severely diminishing quality of life.
Estimates suggest that 4-5% of the global population is affected by asthma. In India, the prevalence stands at approximately 2%, translating into a formidable burden impacting over 15 million patients. While conventional medical treatments, such as steroids and inhalers, offer symptomatic relief, they frequently entail biological side effects, complications, and foster dependency on pharmaceutical interventions. This pressing reality underscores an urgent demand for innovative and holistic therapeutic strategies that not only mitigate symptoms but also address the root causes while minimizing adverse effects.
Homoeopathy, in contrast, embraces a holistic treatment philosophy. It tailors treatment to the individual, administering a “similimum”—a remedy chosen based on the unique symptomatology and constitution of each patient, applied in a minimum, effective dose. Crucially, in chronic diseases like asthma, where a case may reach a therapeutic plateau or a latent disease state persists even after the administration of the constitutional similimum, the concept of “intercurrent remedies” becomes vital. As elucidated by Dr. Stuart Close, the strategic use of anti-miasmatic and nosode remedies as intercurrents can penetrate these latent layers, yielding profound and sustainable improvements by addressing the underlying disease predispositions.
Primary Study Aim
The overarching objective guiding this research endeavors to…
Key Study Objectives
To achieve the primary aim, several specific objectives were established to comprehensively evaluate the role and impact of intercurrent remedies.
- To understand the effectiveness of intercurrent remedies in homoeopathic management in cases of bronchial asthma.
- To study the relevance of intercurrent remedies of Stuart Close in cases of bronchial asthma, emphasizing their theoretical basis and practical application.
- To improve the quality of life in the patients suffering from bronchial asthma, assessed through validated clinical tools.
Methodology: A Rigorous Approach to Clinical Investigation
This pilot study meticulously followed a prospective experimental design, implementing a precise protocol from patient recruitment to final outcome assessment. This systematic framework was crucial for ensuring the reliability and validity of data collected concerning the efficacy of intercurrent remedies.
Study Type: Prospective Experimental Study
Sampling: Random Sampling for Representative Data
Sample Size: 12 Patients Selected
Study Location: Sainth Homoeopathic Hospital, Rajkot
Patient Recruitment: Based on Defined Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
Initial Assessment: Utilizing Asthma Control Test (ACT) for Baseline
Therapeutic Intervention: Similimum & Intercurrent Remedies
Follow-up Schedule: Every 15 Days (with Flexibility)
Data Analysis & Conclusion: Rigorous Evaluation of Outcomes
Inclusion Criteria
The following stringent criteria were applied to ensure a focused and relevant patient cohort for the study.
- Pre-diagnosed cases of bronchial asthma confirmed by comprehensive clinical history, presentation, and physical examination findings.
- Patients with diagnosed asthma currently under conventional treatment but experiencing uncontrolled symptoms, who express a desire to transition to Homoeopathy.
- Participants aged between 15 and 45 years at the time of enrollment.
- Both male and female sexes were included to ensure broader demographic representation within the study limitations.
Exclusion Criteria
To maintain the purity of the study’s intervention and mitigate confounding factors, specific patient conditions or concurrent treatments led to exclusion.
- Patients diagnosed with bronchial asthma complications necessitating oxygen therapy or emergency intervention.
- Individuals outside the defined age range: younger than 15 years or older than 45 years.
- Patients with any co-existing malignant medical conditions.
- Individuals currently receiving or with a recent history of oral or injectable steroid therapy for asthma or related conditions.
- Patients with underlying cardiac complications that could influence asthma management or outcomes.
- Pregnant women, due to ethical considerations and potential physiological complexities affecting asthma presentation.
Demographic Insights of the Study Cohort
Understanding the demographic composition of the study participants is crucial for interpreting the results and assessing their generalizability. This section details the gender and age distribution of the 12 enrolled patients.
Patient Gender Distribution
The majority of the study cohort consisted of male participants.
Out of 12 participants:
8 Males (66.6%)
4 Females (33.3%)
Patient Age Distribution
The study predominantly included younger adult patients within the specified age range.
Out of 12 participants:
-700″>Age Group Distribution:15-25 years: 9 patients
26-45 years: 3 patients
Therapeutic Interventions: Prescribed Remedies
This section delineates the specific homoeopathic remedies utilized throughout the study, categorizing them into baseline prescriptions (similimum) and the crucial intercurrent remedies employed to address deeper miasmatic layers or therapeutic plateaus.
Frequency of Baseline Homoeopathic Drugs
The initial homoeopathic remedies most frequently prescribed upon patient enrollment, reflecting the constitutional similimum choice.
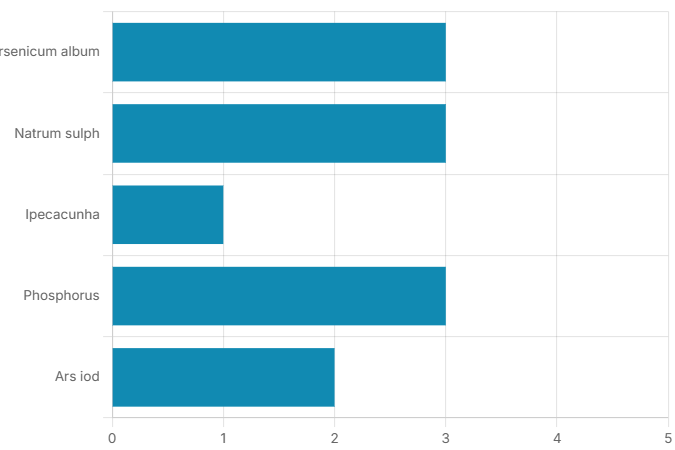
Arsenicum album & Phosphorus: Each prescribed to 3 patients, indicating their strong symptom-matching in this cohort.
Natrum sulph: Also used for 3 patients, reflecting its relevance in specific asthmatic presentations.
Ars iod: Prescribed for 2 patients, suggesting its utility in particular nuanced cases.
Ipecacunha: Used for 1 patient, indicating a less frequent but still relevant remedy.
Frequency of Intercurrent Remedies Prescribed
Highlighting the crucial intercurrent remedies utilized to address latent disease phases and facilitate deeper healing as per Dr. Stuart Close’s principles.
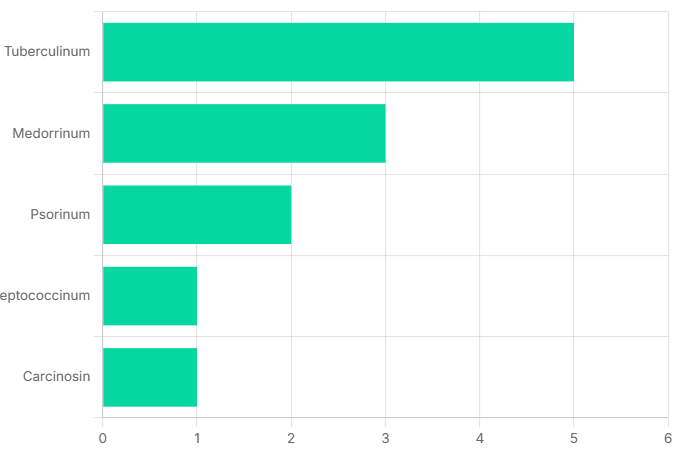
Tuberculinum: Most frequently used for 5 patients, emphasizing its role in addressing tubercular miasmatic influences.
Medorrinum: Prescribed for 3 patients, targeting sycotic miasmatic background.
Psorinum: Used for 2 patients, indicating its application for psoric miasmatic blocks.
Steptococcinum & Carcinosin: Each used for 1 patient, demonstrating a tailored approach to specific miasmatic challenges.
Study Outcomes: Assessing Efficacy and Patient Progress
The effectiveness of the homoeopathic intervention was rigorously assessed through overall patient outcomes and the standardized Asthma Control Test (ACT) scores. This section presents a detailed analysis of these key indicators, reflecting the study’s impact on patient health.
Overall Patient Outcome Distribution
A comprehensive summary of the primary outcomes following the homoeopathic intervention, highlighting the proportion of patients who experienced improvement.
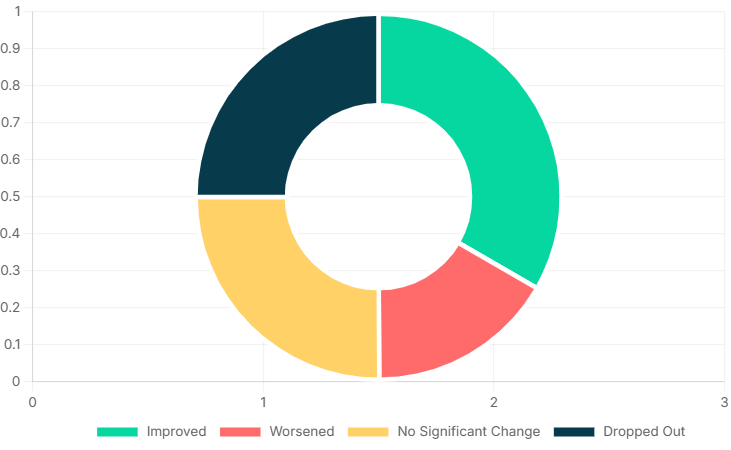
| Outcome Category | Number of Patients | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Improved | 4 | 33.3% |
| Worsened | 2 | 16.6% |
| No Significant Change | 3 | 25.0% |
| Dropped Out | 3 | 25.0% |
Asthma Control Test (ACT) Score Improvement
The ACT score is a vital tool for objectively assessing asthma control levels. This visualization illustrates the distribution of patients across different control categories post-intervention, indicating a discernible shift towards improved management for a portion of the cohort.
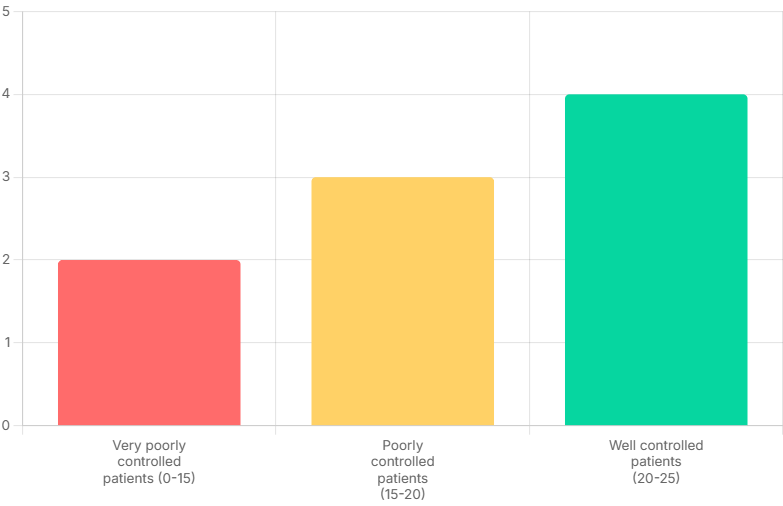
Very Poorly Controlled (0-15): Indicates severe asthma symptoms with substantial impact on daily functioning. In this study, 2 patients remained within this category.
Poorly Controlled (15-20): Suggests moderate asthma symptoms necessitating enhanced management strategies. 3 patients were identified in this group, indicating room for further improvement.
Well Controlled (20-25): Represents optimal symptom control and minimal impact on daily life. A significant positive outcome was observed for 4 patients in the study, showcasing the effectiveness of the intervention for this subgroup.
The effectiveness of the homoeopathic intervention was rigorously assessed through overall patient outcomes and the standardized Asthma Control Test (ACT) scores. This section presents a detailed analysis of these key indicators, reflecting the study’s impact on patient health.

Figure: Asthma Control Test (ACT) Questionnaire used for assessment.
Conclusion: Advancing Homoeopathic Efficacy in Asthma Management
This pilot study offers compelling evidence that the integrated homoeopathic approach—combining a meticulously selected constitutional similimum with the strategic application of intercurrent remedies (such as nosodes)—yields positive therapeutic outcomes in bronchial asthma cases. This methodology, rooted in the profound principles articulated by Dr. Stuart Close, demonstrates a capacity for deeper, more sustained healing beyond symptomatic palliation. The findings underscore the potential efficacy of this specific homoeopathic intervention in contributing to the comprehensive management of bronchial asthma, addressing not only overt symptoms but also underlying miasmatic predispositions. While promising, these observations necessitate further expanded research, including larger cohorts and randomized controlled trials, to rigorously validate and broaden the applicability of these significant results in the global clinical landscape.
References
- sarkar B.K., Organon of Medicine, 10th reprint ed. 2011; Birla publication,p116,119,164.
- Hahnemann Samuel. Organon of Medicine. 6th ed. B. Jain Publishers; 2002.
- Hahnemann S. The Chronic Diseases, Their Peculiar Nature and Their Homoeopathic Cure. 1904
- Stone RM, Tinsley Randolph Harrison, Netlibrary I. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine: self-assessment and board review. New York: Mcgraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division; 2001.
- Loscalzo J, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 21st ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2022.
- R. Mcintyer, BS MD, Close S. The Genius of Homoeopathy. B. Jain Publishers; 2001.
- Asthma Control Test (ACT) \[Internet]. www.thoracic.org. Available from: https://www.thoracic.org/members/assemblies/assemblies/srn/questionaires/act.php